Unmet need

Reference
Ghaferi AA, Birkmeyer JD, Dimick JB. Variation in hospital mortality associated with inpatient surgery. N Engl J Med 2009;361:1368-75.

Of postoperative deaths occur in the general medical / surgical wards. ⓘ
Reference
Spence et all. CMAJ 2019

Of complications in hospitalized patients are potentially preventable. ⓘ
Reference
Baker, G. R., Norton, P. G., Flintoft, V., Blais, R., Brown, A., Cox, J., Etchells, E., Ghali, W. A., Hébert, P., Majumdar, S. R., O'Beirne, M., Palacios-Derflingher, L., Reid, R. J., Sheps, S., & Tamblyn, R. (2004). 4) The Canadian Adverse Events
Study: the incidence of adverse events among hospital patients in Canada. CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne, 170(1 1), 1678-1686.

Days prolonged stay in the hospital after complications (serious adverse events). ⓘ
Reference
Lilian HF Hoonhout et al. SAEs cause 4 days prolonged stay in hospitals. Direct medical costs of adverse events in Dutch hospitals, BMC Health Services Research volume 9, Article number: 27 (2009)
Current manual monitoring practice far from reveals all clinical deterioration
Current monitoring of vital signs (heart rate/pulse, respiratory rate, peripheral oxygen saturation, temperature, blood pressure) is insufficient.
Major surgery and acute medical disease entail substantial risk of complications and mortality. Manual monitoring is far from reveals all clinical deterioration.
Manual data interpretation cannot capture trends and combination of several physiological parameters. ⓘ
Reference
Nielsen et al. Review of Early Warning Score in preventing sudden critical illness and death.
Gerry et al. Early warning scores for detecting deterioration in adult hospital patients: systematic review and critical appraisal of methodology. BMJ 2020;369:m150.
McGaughey et al. Early warning systems and rapid response systems for the prevention of patient deterioration on acute adult hospital wards.
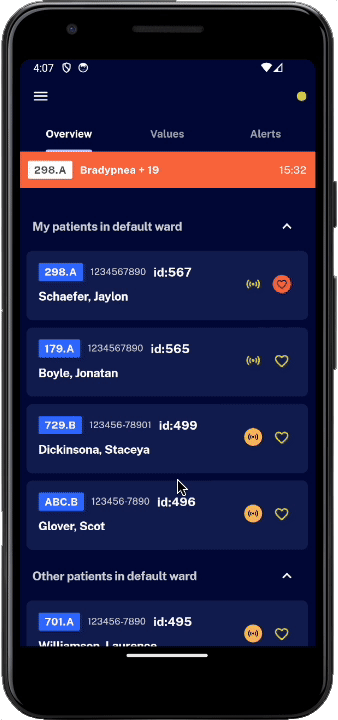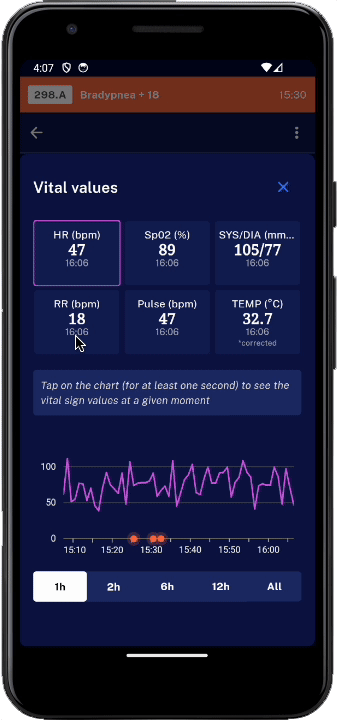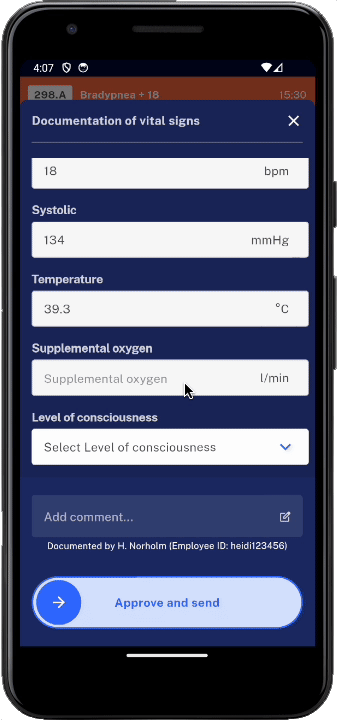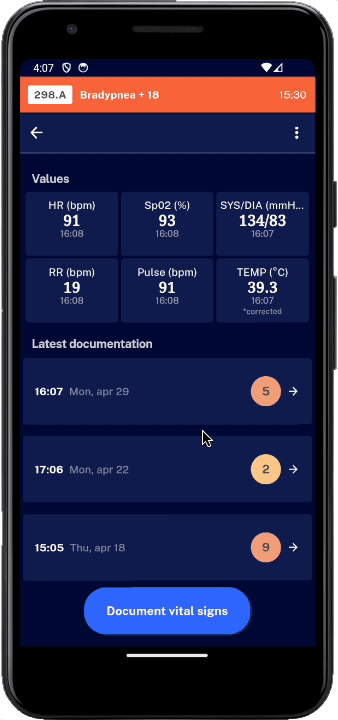
Our solution and product
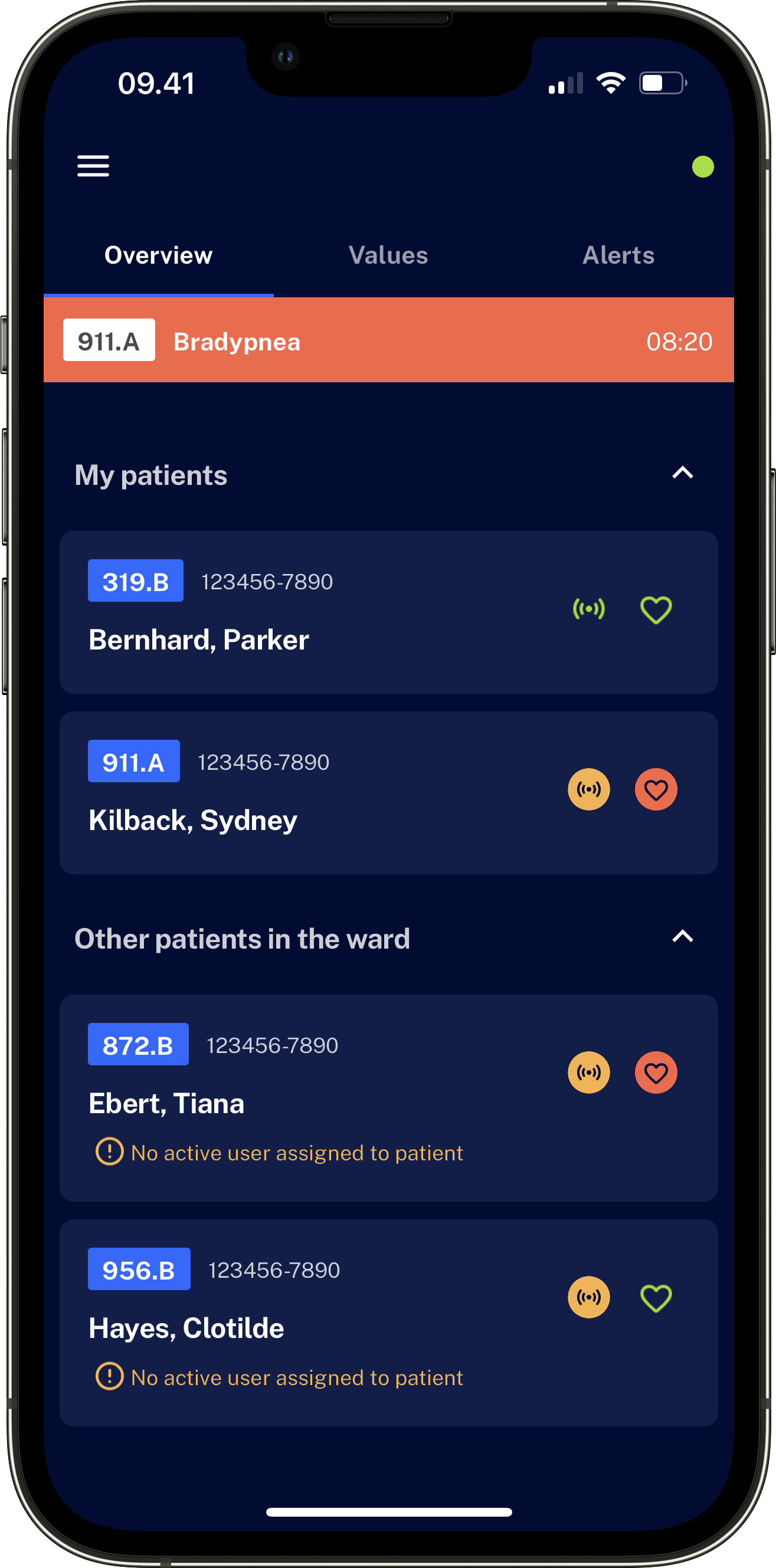
Using advanced clinically modelled algorithms to monitor patients with with WARD Clinical Support System (WARD-CSS).

Medically certified
WARD-CSS is a CE-certified Class IIa SaMD product.

EU MDR approved

ISO 13485 compliant

WARD-CSS CE

Advanced clinically modelled algorithms interpret vital sign patterns in real-time from wireless sensors and detect deterioration earlier.
Integrating sensors:
Integrating with already marketed sensor equipment: Turning continuous monitoring into clear overview and actionable alerts
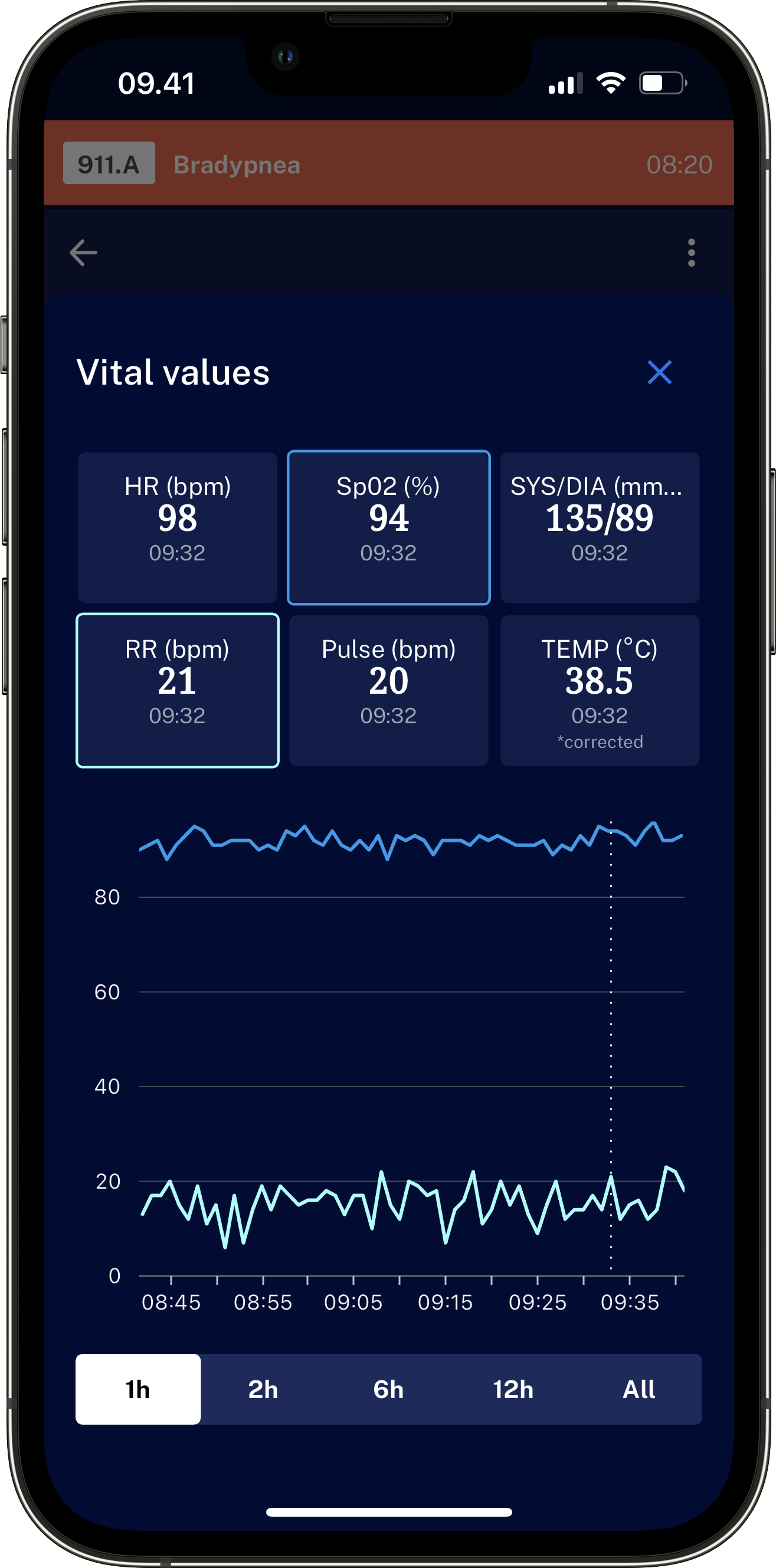
Locked screen or open app:
WARD-CSS notifies the Health Care Professional in a manageable way

Clinically validated, algorithm-based software transforming patient monitoring

Benefits with WARD-CSS
Meet our dedicated team
At WARD 24/7, our team is composed of passionate and skilled professionals dedicated to transforming patient monitoring and improving healthcare outcomes.

Betina Langemark
Co-founder & CEO

Jelle Reichert
Co-founder & CTO

Michael Frandsen
CCO
Our partners
We are a partner in the WARD Project - an InnovationFund Denmark supported Grand Solution project.
© All Copyrights 2024 by Ward247.com




